Stroke is the third greatest cause of death, behind cancer and heart disease. A stroke or its complications account for about one-fourth of all stroke patients' deaths. Uncontrolled diets high in saturated and trans fats that result in cholesterol buildup in the arteries and excessive blood pressure are the main contributors to stroke. In other words, if the buildup of cholesterol in the arteries prevents blood from reaching any region of the body, preventing the brain from receiving oxygen, resulting in the death of some brain cells, and stopping those cells from procreating, then we have a hit. When a blood vessel in the brain bursts, it depletes the brain's cells of oxygen, resulting in a mild stroke.
Symptoms of Stroke
1. Suddenly having trouble standing
The sudden depletion of oxygen-carrying blood due to artery narrowing and high blood pressure causes unexpected difficulties standing, which is an early sign of stroke.
2. Lightheadedness and instability
The brain combines data from the eyes, inner ear, and other senses to maintain balance. Dizziness and loss of balance will happen if the cells in this area of the brain are destroyed as a result of a lack of oxygen.
4. Having issues communicating and comprehending
When brain cells in the Broca, Wernicke, and Angular Cyrus areas of the left hemisphere start to die because they no longer receive the oxygen and nutrients they require to operate, difficulty speaking and understanding results.
5. Quickly worsening headaches
A headache is a painful condition that usually affects the head, though it can occasionally cause neck or upper back pain. Although it is one of the most frequent local pains and can affect many people, sudden, severe headaches can also result from a broken blood vessel in the brain, oxygen deprivation in certain body areas, or sudden heart disease, as we have highlighted in earlier articles. brain.
For assistance in resolving these symptoms, speak with your Stroke Specialist in Coimbatore.
Stroke Types
There are two types of stroke.
- A clot or other obstruction in an artery leading to the brain is what causes an ischemic stroke.
- A brain vessel ruptures as a result of blood pouring into the brain, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
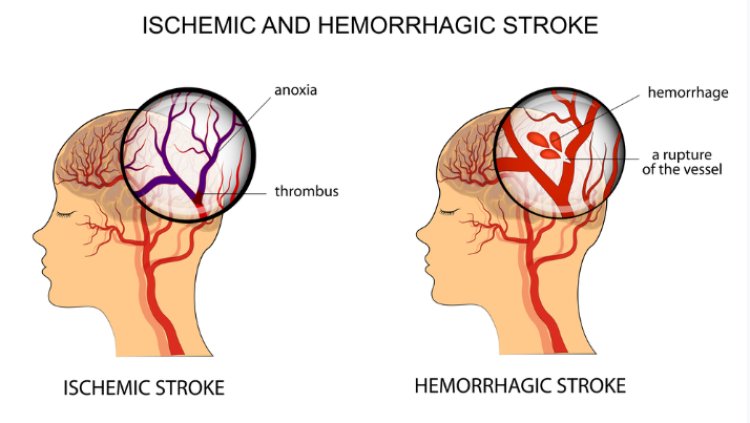
Ischemic stroke
It accounts for around 80% of all strokes, making it the most prevalent form. The arteries that supply the brain with new blood from the heart and lungs are crucial. The blood transports nutrients and oxygen to the brain while also removing carbon dioxide and cell waste. The brain cells may not receive adequate oxygen if an artery is clogged. They finally run out of power because they are unable to produce enough of it.
Hemorrhage Stroke
A blood vessel inside the brain bursts to cause a hemorrhagic stroke, which puts more pressure on the brain and damages it by pressing it up against the skull. High blood pressure is linked to hemorrhagic stroke because it strains artery walls to the point of rupture. If you want detail about hemorrhage stroke kindly click the link Hemorrhage stroke - overview
Stroke Treatment
An emergency brain stem stroke will receive the appropriate treatment depending on the type of stroke. determine whether the stroke is hemorrhagic (brain hemorrhage) or ischemic (artery blockage).
Treatment For Ischemic Stroke
The goal of treatment for an ischemic stroke is to reestablish blood flow to the brain. This could be accomplished by using drugs that break up clots. The most common form of treatment for ischemic stroke is an intravenous injection of alteplase, a recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Procedures carried out inside the obstructed blood vessel are sometimes used to treat ischemic strokes. Other procedures like a carotid endarterectomy or an angioplasty may be performed depending on the medical condition.
Treatment For Hemorrhagic Stroke
The doctor attempts to stop the bleeding and lower the pressure in the brain in the event of a hemorrhagic stroke. Brain Stroke Surgery might reduce potential risk. Treatments for brain stroke include surgical coiling, clipping, removing AVMs through surgery, and stereotactic radiosurgery.

Comments
Post a Comment